15 20 30 40 45 50 60 mostly
A2011, aluminum-copper alloy, free-cutting alloy with excellent machinability but strong corrosion resistance.
A2017, aluminum-copper alloy, high strength, good processability, hard aluminum.
A5052, an aluminum-manganese alloy, is a medium-strength, most representative aluminum alloy with high fatigue strength and excellent seawater resistance.
A5056, an aluminum-manganese alloy, has excellent seawater resistance and good surface treatment after cutting.
A6061, aluminum-manganese-silicon alloy, heat-treatable corrosion-resistant alloy, has strong corrosion resistance after T6 treatment.
A6063, an aluminum-manganese-silicon alloy, has lower strength than the extruded A6061, but has superior extrudability and can be formed into various complex cross-sectional shapes. It also has excellent corrosion resistance and surface treatment properties.
A7075, an aluminum-zinc-manganese alloy, is one of the strongest aluminum alloys, but has poor corrosion resistance and is a super-hard aluminum alloy.
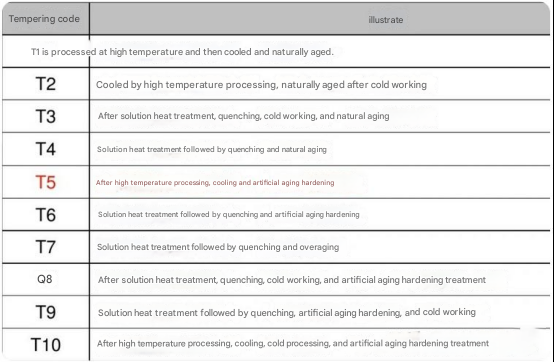
Solution heat treatment:It is a heat treatment process in which the alloy is heated to a high temperature so that the components in the alloy dissolve evenly in the solid state to form a uniform solid solution, and then rapidly cooled to maintain this dissolved state.
Artificial aging refers to the process of heating a solution-treated alloy to an appropriate temperature above room temperature and holding it for a certain period of time to change the alloy's properties. During this process, the structure between the metal atoms changes, thereby optimizing the alloy's mechanical properties and stability.
The wall thickness of each manufacturer will be different. Generally speaking, the conventional ones are 1.5, 1.8, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.2, 3.5, and 4.0.
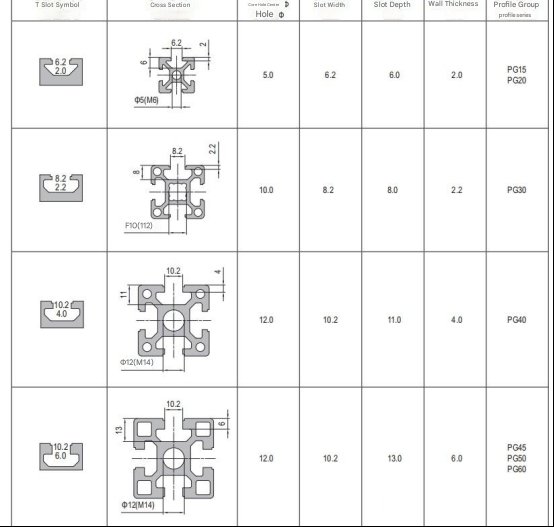
There are two points to understand here:
1. The axial hole of the aluminum profile is generally designed according to the bottom hole of the screw thread. Therefore, the hole can be used directly after tapping.
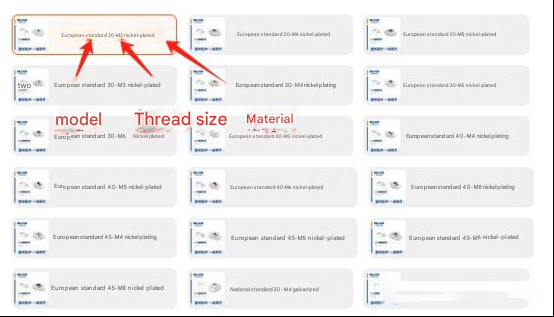
2. When purchasing T-nuts, you only need to match the model and select our thread size and material. The nut shape can match our slot size, as follows:
Note: As shown in the figure above, the letters behind the 4040 aluminum profile represent different thicknesses and weights per meter, which need to be filled in according to actual needs. The above takes the 40 type as an example. Even if it is the same model, the specifications of 4040 are many.
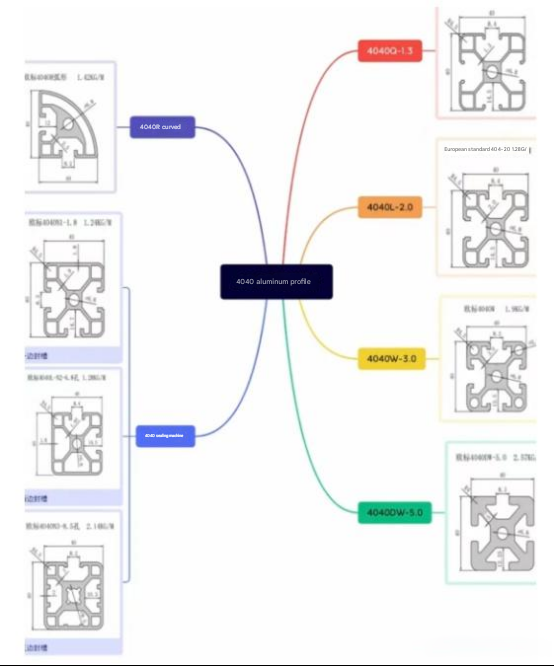
The applicable scope of different thicknesses is also different.
|
Thickness (mm) |
Common application areas |
|
1.5 |
It is suitable for frame combinations with low stress and strength, and is often used in the production of assembly line workshop workbenches and production management signboard frames. |
|
2.0 |
Used in frame structures that require a certain strength but are not heavy-loaded |
|
2.5 |
Suitable for medium strength and load-bearing occasions |
|
3.2 4.0 |
Suitable for frame structures with high stress and strength, such as equipment rack frame production |








There are a few things to focus on about accessories:
About nuts: There are several types of profile nuts, and the various styles are designed to suit different installation requirements and working conditions.
About the cover: The cover will take up space, so in order to prevent it from protruding during design, it is necessary to reserve a cover thickness at the joint to install the cover to achieve an aesthetic effect,and it needs to be clearly marked on the assembly drawing to avoid mistakes by the assembler.
Note: Basically, the accessories required for connecting aluminum profiles have been made into standard parts.
Mechanical calculation:
The load-bearing capacity of aluminum profiles is mainly measured by deflection in the industry.Misumiprovides two calculation methods:
A. Chart query method (simple and operational, but the limitation is that it requires the use of Misumi profiles).

Here are a few key points:
Just follow the steps to calculate
As long as the deflection amount indicated in the steps is less than the use length L/1000, the use requirements are met (this sentence is the key).That is, if your use length is 500mm, and the deflection amount you calculated is 0.4, then you meet the requirements, 0.4<0.5. Of course, for safety reasons, you still need to set a safety factor.
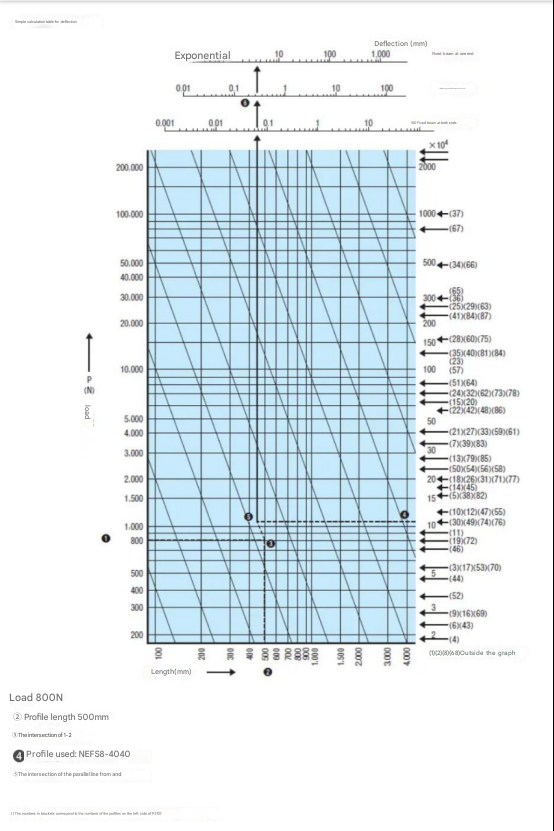
How to calculate using the above table?
Known parameters: our load (N), what aluminum profile we preselected (specifications), the length of our aluminum profile L (mm)
Installation method: The support method of the aluminum profile. As shown in the figure below, the more solid the support method, the smaller the deflection will be. The best method is to fix it at both ends.
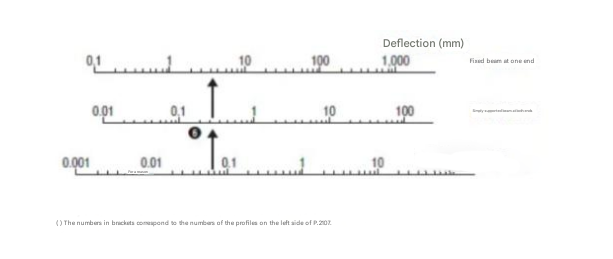
This is the table below. Each specification has a number.
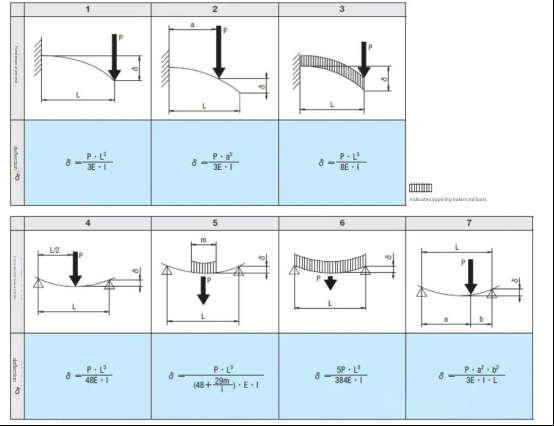
B. Calculation method: The following is the calculation formula for the deflection amount of different support methods (generally applicable):

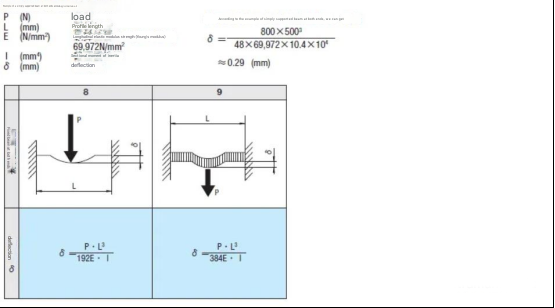
The calculation only requires substituting the known data. We all know the load and length. Let me explain Young's modulus and section moment of inertia.
Young's modulus: The Young's modulus of aluminum is a property value, just like density. Although there are many grades of aluminum, we can all regard it as 70,000/mm².
Sectional moment of inertia: MISUMI has provided a table and a chart with data for the selection method. However, we need to note that in reality, we cannot all afford MISUMI’s aluminum profiles, and the thickness specifications of aluminum profiles on the market vary. Therefore, we can refer to MISUMI’s table to convert our actual aluminum profile thickness by comparing it with MISUMI’s models of the same specifications, and multiply it by a certain coefficient to convert our section moment of inertia.
Finally, by substituting all the data, we can know whether the aluminum profile we choose is suitable. If it is not suitable, we can consider reducing the length or choosing a larger specification to modify our plan.
Assembly of aluminum profiles: Please refer to the actual installation method and go to the workshop and ask the master craftsman to install it.
In our design process, there are commonly used aluminum profile sections. We only need to put the folder in the corresponding position of the SW installation folder to call the SW profile library.
Q: Can aluminum alloy profiles be cut to a specified length? What is the cutting accuracy?
A: Any length between 50~4000(mm) can be specified (specified in 0.5mm units) for cutting, and the cutting tolerance is within ±0.5mm.
(Specific details depend on the manufacturer's cutting equipment, please consult the processor)
Aluminum profiles are generally priced by the meter, with a maximum length of 6m, and can be cut individually.
Special blades are required to cut aluminum profiles. Generally, the surface of the cuts made by grinding wheels will not be glossy and the aluminum will stick to the grinding wheel.
Q: Can the color of aluminum profiles be customized?
A: Black and silver are commonly used, and there are also matte and glossy finishes. Customization is also possible, but the cost is higher.
Q: I have a periodic reciprocating motion mechanism with a load of 200kg and a starting acceleration of 2m/s². Can I use aluminum profiles to build a frame?
A: It is not impossible to use aluminum profiles to build a shelf, but after all, it is spliced. If conditions permit, it is recommended to use welded parts or castings if high rigidity requirements are required.
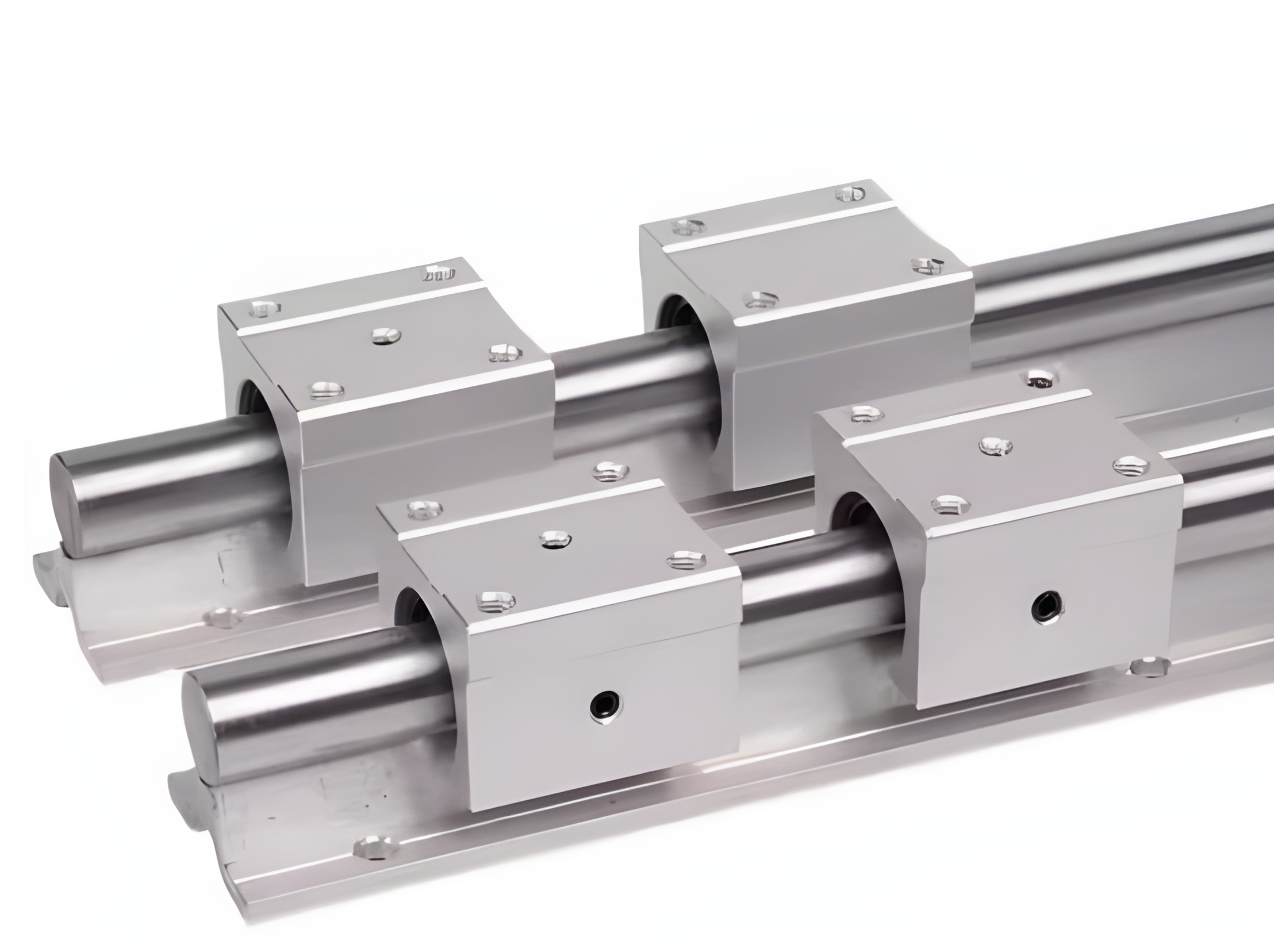
Q: Can linear guides be installed on aluminum profiles? What is the accuracy?
A: First, let’s understand the stroke accuracy, as shown below:
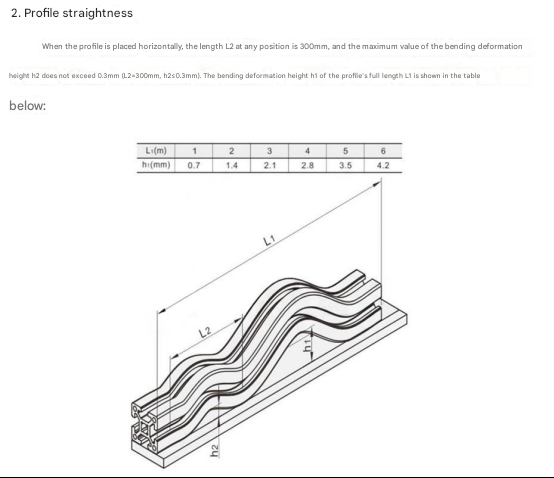
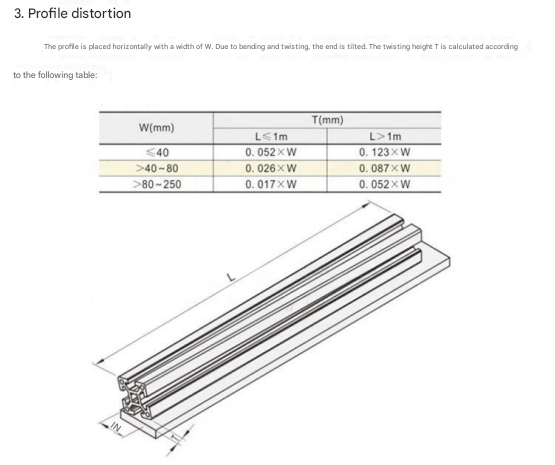
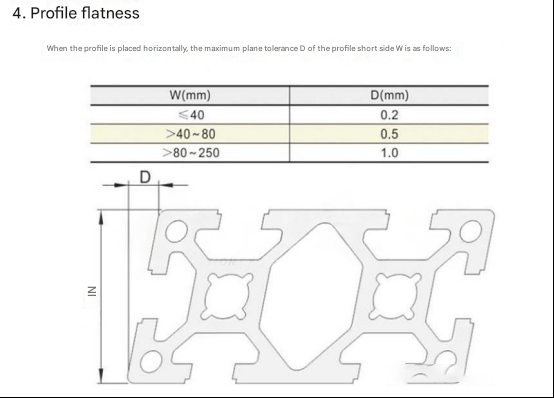
From the above drawings, we can know that the precision of aluminum profiles is not high, and it is not at the same level as the precision of linear guide rails. Therefore, it can be considered forapplications with low precision, low load, medium and low speed, and smooth movement. For this reason, even if positioning or limiting parts are added, it can only be said that a certain degree of stability and assembly convenience are improved. After a long period of operation, it is still uncontrollable, and the precision is essentially not up to par.
If you really want to use this aluminum profile as a base and require precision, you can meet the requirements byprocessing the installation reference surface and adding inserts .
In addition, if it only bears vertical loads, we can also use aluminum support optical axis guide rails as a substitute.
